Google has announced this year that Core Web Vitals will be the new ranking factor in next year 2021.
What are Core Web Vitals?
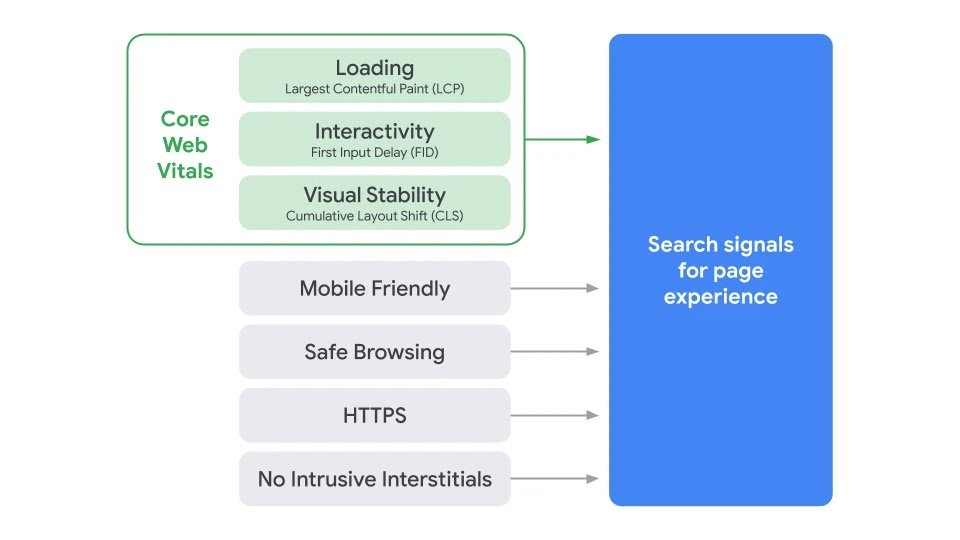
Core Web Vitals are a set of upcoming ranking factors that Google considers important in a web page in view of the user’s overall experience.
The basic measurement factors of Core Web Vitals are based on a specific page speed, and user’s interaction.
So here are the three important factors.
- Largest Contentful Paint
- First Input Delay
- Cumulative Layout Shift
So, today’s content will be based around the above mentioned measurements, and I will try to make you understand all these three factors one by one.
If I will make it simple, Core Web Vitals are a set of factors that is part of Google’s Page Experience, basically a factor defined by Google to measure a webpage’s overall UX.
Core Web Vitals are basically a replacement of factor “Page Speed” which was available in Search Console previously, but now it’s showing as Core Web Vitals there.
Here is the snip of Core Web Vitals in Search Console:
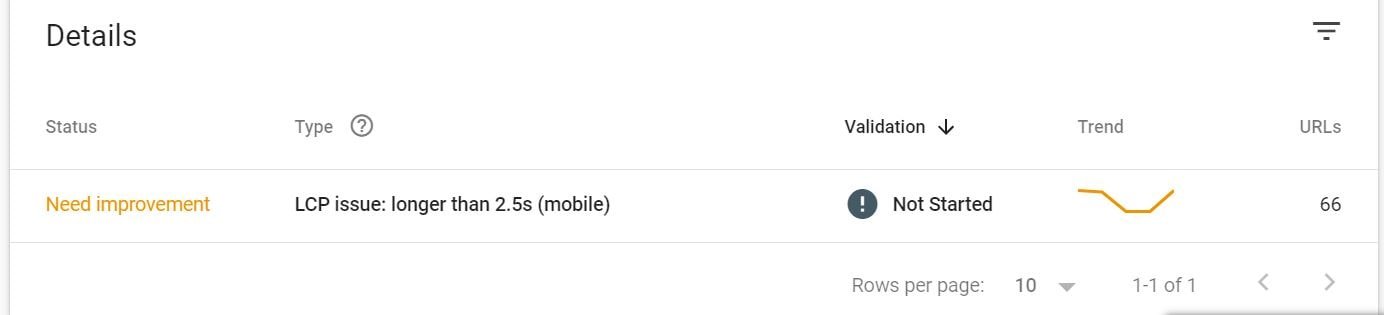
Once you click on the Core Web Vitals, you can see the Good URLs highlighted Green, Yellow Highlighted needs improvements and Red highlighted URLs are showing as poor as the below screenshot.

Once you go below to this graph, you will find the details sections here where you will find the issue with your webpage as why they are showing red or yellow just like below snip.
Why do you need to take Core Web Vital Serious?
Google has announced that Core Web Vitals will be an official ranking factor from next year i.e. 2021.
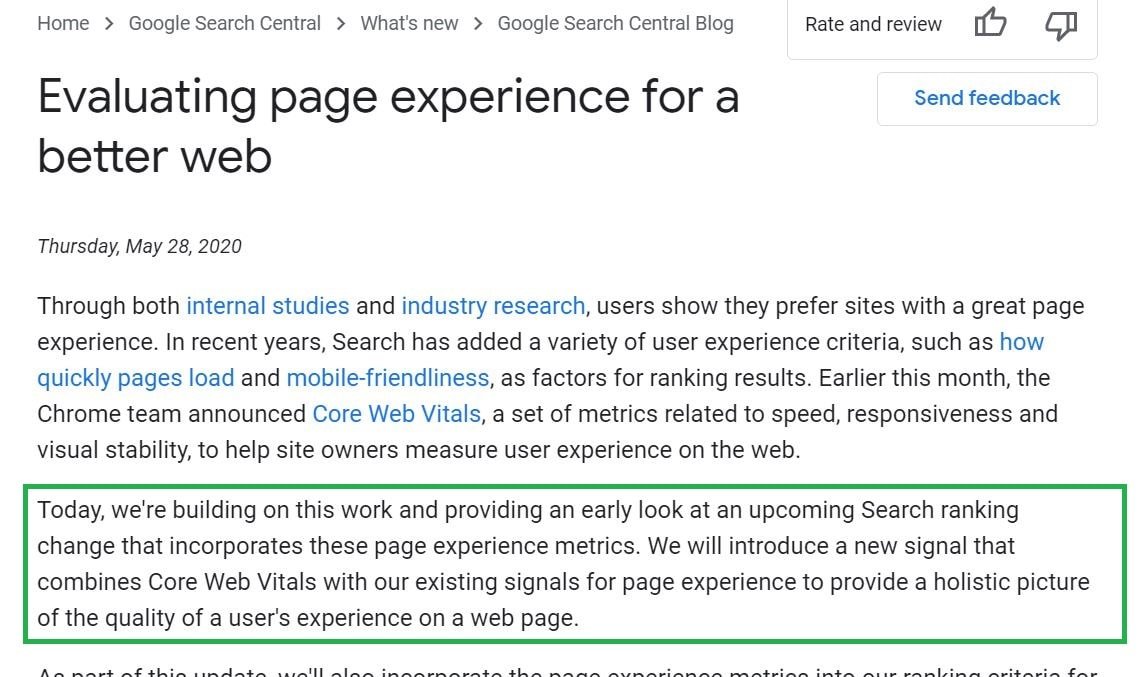
you can read a full article by clicking on the link shown below:
https://developers.google.com/search/blog/2020/05/evaluating-page-experience
The new page experience will be purely based on the new factors which are Core Web Vitals altogether the below factors will work together to decide your page performance further.
- Mobile Friendliness
- Safe browsing
- HTTPS- Security
- Intrusive interstitial guidelines
And Core Web Vitals will be a most important matrix to evaluate your page score.
As the Name itself suggests that the Core Web Vitals will be the most important chunk of a webpage experience score.
So let’s describe the Core Web Vitals in details:
Largest Contentful Paint:
Largest Contentful Paint measures the time which is spent to load a webpage from an actual user’s point of view.
In other simple words, it is the actual time where a web page clicked and most of the contents of a web page has been displayed or loaded.
LCP is different from other page speed matrix as it focuses on the time where a user clicked and is able to see most of the webpage’s content and can interact with a web page.
You can check your LCP score using page speed insight tools from Google.

https://developers.google.com/speed/pagespeed/insights/
A simple understanding tells that you need to optimize your webpage to hit LCP within 2.5 seconds.
The second factor in the list is FID, so let’s explore this further.
First Input Delay:
The second core factor of Core Web Vitals is First Input Delay.
So after the successful achievement of FCP, the next matrix comes into picture where a user has landed on the page and now trying to interact with the page by taking action.
The interaction is a next step for a user to take action on a web page by scrolling the page, clicking on the button or filling the data in a form on a webpage.
Google’s first priority is to serve the best webpage in terms of user experience and this FID matrix is something which is really important as how a user interacts with a web page and navigates further.
FID technically measures how long it takes to perform an action on a webpage. So logically its a page speed score, but here it goes one step complex as it measures the time taken for a user to actually perform a task on a webpage.
For most of the blog pages, it should not be an issue as a user needs to scroll the page as an interaction.
But for other sites like, ecommerce or other where a user needs to interact with a login page, signup page and other can be an issue to manage FID.
Here are some of the examples.
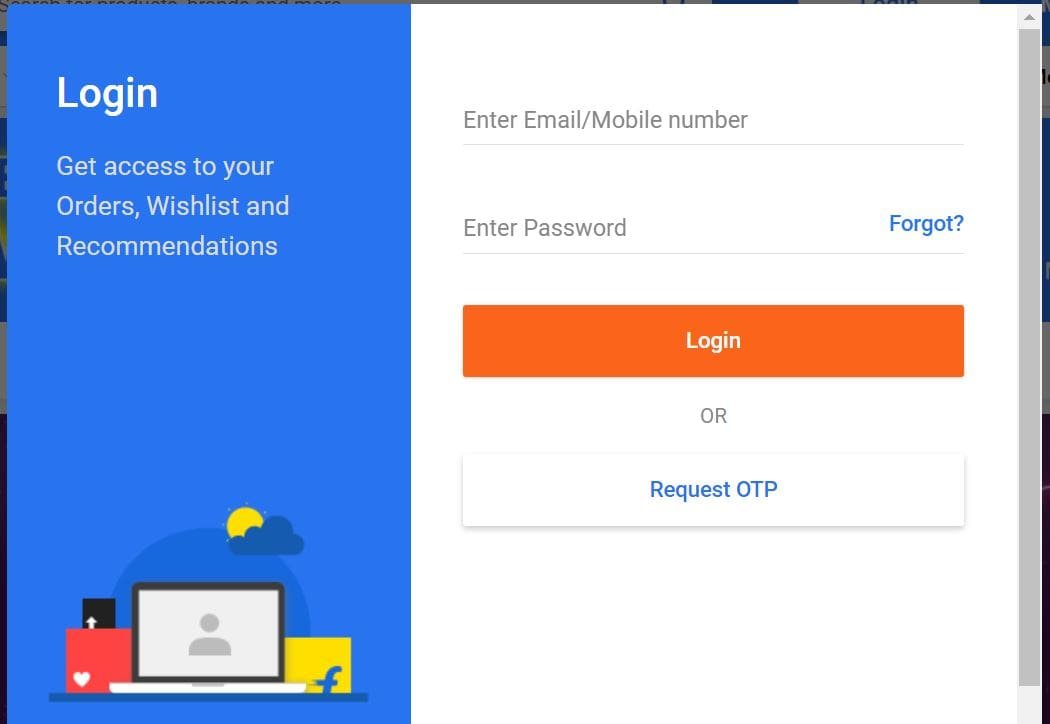
The third matrix of Core web Vitals is Cumulative Layout Shirt ( CLS), lets check it out further how does it works:
Cumulative Layout Shift (CLS)
Cumulative Layout Shift is referring to a webpage’s stability during the process of a page loading.

In other words, a webpage should be load smoothly from up to down, if a webpage’s elements are moving around as the page loads, then this should be a sign of a high CLS which is bad.
I have experienced a lot of web pages from top notch high authority websites, where a user interaction is really poor as they frequently distract a user forcefully by navigating them into their promotional stuff through pop-ups, GIF’s and other fancy links.
These tactics are being used more frequently to promote or sell a product or service, but drastically spoil a user’s experience and most of the time; a user has to leave out that webpage just to avoid this stuff which behaves like zombies.
Altogether sometimes, a web page looks fully loaded, but when a user tries to interact, some other stuff on the page loads and a user unintentionally clicks on an unwanted stuff which also irritates a user and results in a poor user experience.
To improve a user’s experience to your webpage, you need to ensure that a webpage on your site should be fairly stable while loading.
And a user should not be confused to identify where a link, image or other buttons are located when it loads completely or clicks on something by mistake.
It is very important to understand that a great page experience isn’t enough for your webpage to offer a #1 rank in SERP.
But Google is about to make you understand that the page experience is one of the factors of ranking among 200 factors.
You have no need to be frightened from Core Web Vitals, Google announced that you have time until next year to work upon your Core Web Vitals feedback.
However Google also announced that they will intimate well prior approx. six months before its implementation as a full proof Google ranking factor.














Add comment